But still there is a long way to go to achieve the United Nation’s Sustainable Development Goals by 2030 which India is committed to
As many as 85 percent of married women say they decide alone or jointly with their husband how to use their own earnings but only 32 percent of Indian married women between the ages of 15 and 49 are employed as compared to 98 percent of men who are employed. This is one of the findings of the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 5 which was released earlier in the month by Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya.
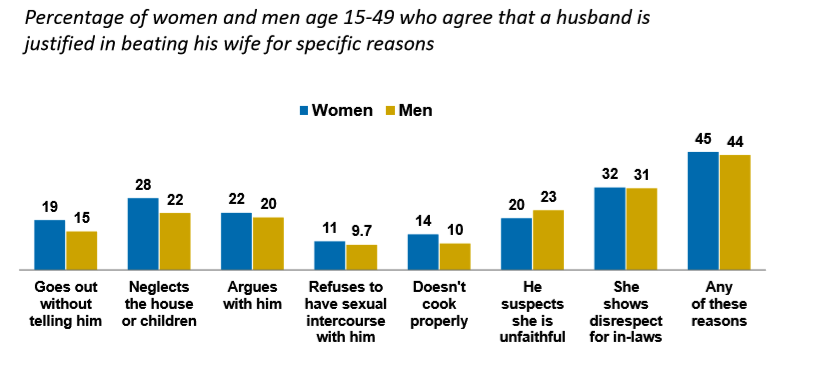
Though there has been a marked improvement in many key indicators survey as far as gender equality and women empowerment is concerned but India is still lagging in attitudes towards violence against women. As many as 45 percent women and 44 percent men justified wife beating in at least one of the seven reasons specified in the survey for the same. But, this is a seven percentage point decrease in women justifying wife beating as compared to NFHS 4 where 52 percent women felt that wife beating was justified. On the other hand there has been a two percentage point increase in men justifying wife beating. It was 42 percent in NFHS 4 but it is 44 percent in NFHS 5.
The reasons for wife beating mentioned in the survey were neglecting house or children, arguing with husband, refusal for sexual intercourse, going out without informing husband, couldn’t cook properly, husband suspected wife of being unfaithful and lastly showing disrespect to in-laws. Among these, the top reason where both men and women agreed that wife beating was justified was for showing disrespect to in-laws at 31 and 30 percentage point respectively. On the other hand the least likely reason for wife beating was for refusing sex where 11 percent women justified wife beating and 10 percent men also agreed that it was a valid reason.
Read More: Afghan Artist Sara Nabil Fights For Women’s Rights
Gender violence, decision making, employment, freedom of movement, access to banking and finance were some of the important parameters to access women empowerment which is also one of the Sustainable Development Goals where SDG 5 is Gender Equality. Dr Mandaviya in his message at the release of NFHS 5 said, “I am also happy to note that NFHS 5 provides information on number of indicators covered in SDGs which India is committed to.” India wants to achieve the SDGs by 2030 so this report is an important resource to understand whether India is on the path to achieving the 17 SDGs by 2030 or not.
A big improvement is seen in the attitudes towards negotiating safer sexual relationships with husband where 80 percent women said that a woman was justified in refusing sexual intercourse with her husband if he has sexual relationships with other women, has sexually transmitted disease or when the wife is not in the mood or is tired. This is a 12 percentage point increase as compared to NFHS 4 when 68 percent believed the same. Compared to this, 66 percent of men agreed that women could say no to sex for any of the three reasons specified in the survey. This is a three percentage point improvement as compared to NFHS 5.
The survey found that 79 percent of women surveyed had a bank or savings account in their name and they themselves operated it. Also, 54 percent of the women owned and operated a mobile themselves. As many as 71 percent of women who owned a mobile could read text messages, indicating their level of literacy. Mobile phone ownership increase sharply with wealth, the survey found. Also, women in states like Goa, Sikkim and Kerala has higher ownership at 91, 89 and 87 percent respectively than states like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh with 39 percent and 41 percent ownership respectively.
On the key indicator of ‘Freedom of Movement’, overall 56 percent of women respondents were allowed to go alone to the market, 52 percent to the health facility and 50 percent were allowed to go outside the village or community. Overall, 42 percent of women surveyed were allowed to go to all three places alone. Only five percent of women were not allowed to go alone to any of the three places specified. But there is only a slight improvement in freedom of movement of women from 41 percent in NFHS 4 to 42 percent in NFHS 5.
It seems freedom of movement of women increases with increase in household wealth but does not consistently vary with education. The movements of younger women are much more restricted than older women according to the survey. As many as 55 percent of women in the 40-49 age bracket could travel alone as compared to 26 percent for girls in 15-19 age group.
Forty two percent of women surveyed own house alone or jointly as compared to 60 percent of men. When it comes to land, 32 percent of women own land alone or jointly as compared to men who own 42 percent of land alone or jointly. Interestingly, rural men and women are more likely to own house or land as compared to their urban counterparts.
The NFHS 5 survey was conducted in 28 states and 8 union territories in 707 districts where 131 key indicators were studied in states/UTs. The survey was conducted in two phases from June 17, 2019 to 30 January 2020 in the first phase and from January 2, 2020 to April 30, 2021 in the second phase. Totally information was gathered from 636,699 households where 724,115 women and 101,839 men were the respondents.










