The term “forks” is being used more often in recent times, especially after the infamous fall of Luna Terra, and its revival. Luna Terra was one of the most stable coins in cryptocurrency. The crash resulted in the loss of $200 billion across the crypto market, with the value of the coins dropping by about 80 percent. The heavy drop made users more curious about forks.
To understand the term forks and what the two different types of forks are, we need to first understand some of the basic terminologies of cryptocurrency.
How Does Cryptocurrency Work?
Cryptocurrency works on the concept of blockchain. The crypto network is decentralised, and works on the concept of peer-to-peer network,which means that the users are responsible for the functioning of the cryptocurrencies. Unlike banks, there is no central authority involved in their working. The account of all transactions is regulated by crypto miners, for which they are rewarded with a good amount of crypto coins.
Technically, the blockchain is the database that is shared across the nodes of a computer network. If we consider the entire crypto network as part of the computer network, each user and its device becomes the node, and every transaction becomes data that is added to a block. The block also contains other information about the transaction such as who transferred the currency to whom, and who received it. It also contains the hash, which is the identity of the block. The next block in the blockchain also contains the previous hash, or the identity of the previous block. This is how the entire ledger of the cryptocurrency is maintained.

Every user enrolled into the specific cryptocurrency has access to this ledger, thus, making it too safe to allow tampering with its details. There are more than 100 million users of cryptocurrency across the world, almost half of whom own a Bitcoin share. Thus, if a hacker tries to tamper the data of the ledger in a blockchain, they would have to hack at least 50 percent of the nodes of that blockchain at the same time, which is seemingly impossible. However, users must be careful with the details of their digital wallets. Just like online scams and thefts, hackers can sift through the data in digital wallets to steal the currency in it.
Forks In Cryptocurrency
Another thing that the crypto market works on is protocols. When the entire crypto world is decentralised and not controlled by any single entity, there is a vital need for definite rules and regulations that the users should follow. These rules and regulations are agreed to consensually by all the users.
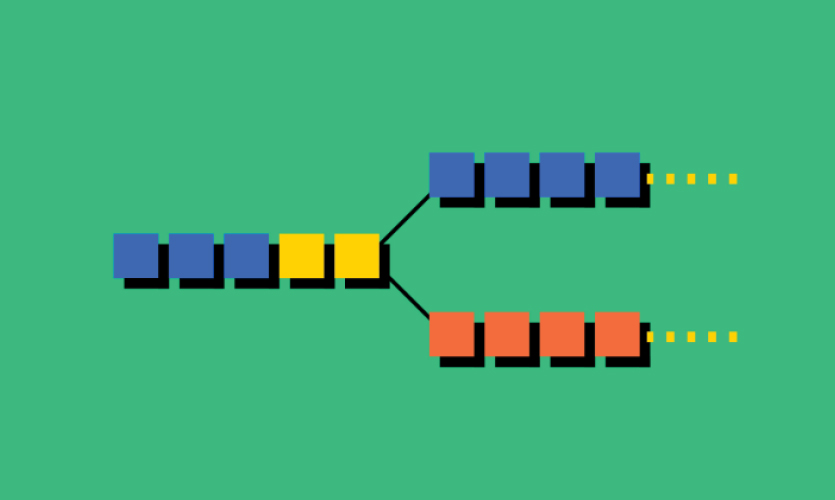
However, when clashes erupt between users, regarding the acceptance of these protocols, a fork is formed. Basically, a fork forms when a group makes changes in the protocol of a certain blockchain. In such case, the blockchain breaks and splits into two separate blockchains, but the original blockchain shares the data history to the new blockchain too. The second blockchain contains a new or updated set of rules or protocols, and creates another path.
Many digital currencies operate through their own development teams that ensure timely changes and improvements in the usage of the currency. It is similar to the application updates on a mobile phone. Thus, a fork is formed in order to secure cryptocurrencies, or add new features to them.
Types Of Forks
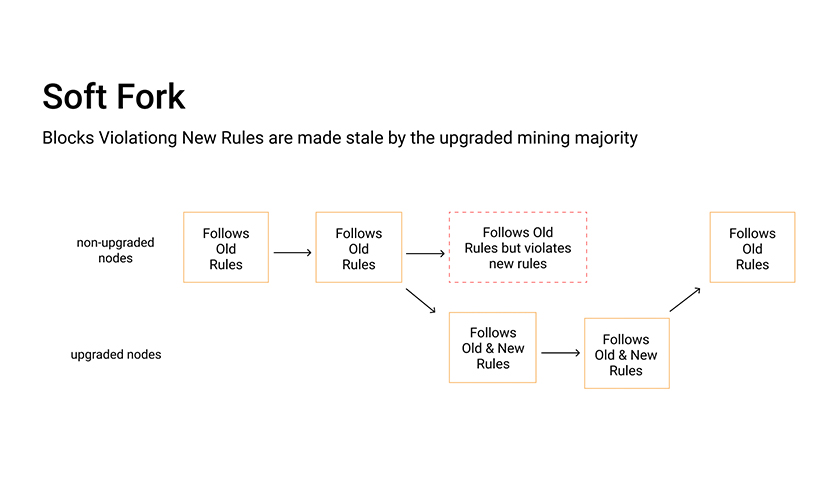
There are two types of form formation, soft forks and hard forks. Soft forks are the updates in the features of the blockchain that are accepted by all the users of that cryptocurrency. The most important feature of a soft fork is that the changes are compatible. It is possible for the individual to simultaneously use the prototypes of both the blockchains. Soft forks are usually used to introduce new features in the blockchain. Such minor changes have been made in currencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum time and again. However, the end result is a single blockchain which has backward compatible changes with pre-blocks.
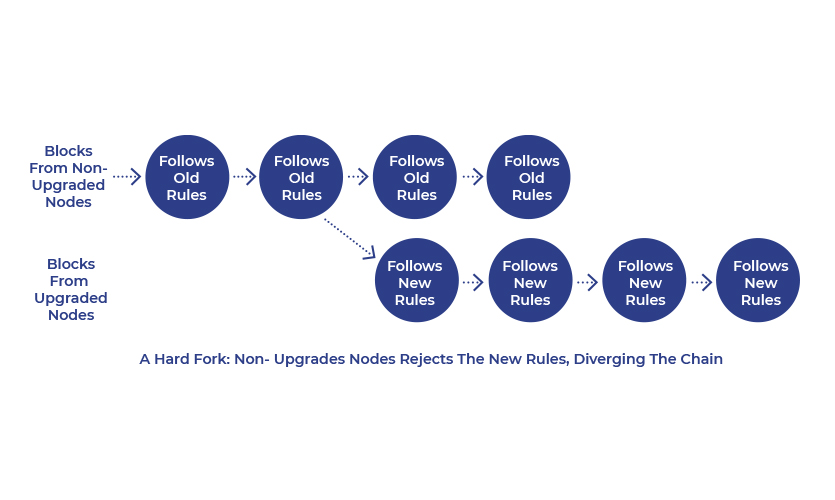
Similarly, hard forks are also the updates in the features or protocol of the blockchain. However, unlike soft forks, hard forks are backward-incompatible. In this situation, the user makes a choice to either continue with the original classic blockchain, or update the prototype and choose a new blockchain. The blockchain forms a complete new path. Although it has the data from the original blockchain, it nullifies any previous protocol of the blockchain. Basically, the user has to update the blockchain and agree to set a new version of the prototype. This also creates an entirely new cryptocurrency. A similar hard fork was added to Bitcoin in 2017, when Bitcoin Cash was introduced. Later other versions such as Bitcoin Gold were also formed through a hard fork. It is worthy to note that if the user updates to a new blockchain, the data from the previous blockchain is also copied. Thus, the user can use the coins from the original currency if he moves to the updated version of currency.
Read more: Indian Government Gets One Step Closer To Introducing Cryptocurrency Regulations